Entrenamiento de modelos en sklearn con GridSearchCV y MLflow#
Ultima modificación: Mayo 14, 2022
Carga de datos#
[1]:
def load_data():
import pandas as pd
url = "http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/wine-quality/winequality-red.csv"
df = pd.read_csv(url, sep=";")
y = df["quality"]
x = df.copy()
x.pop("quality")
return x, y
Particionamiento de los datos#
[2]:
def make_train_test_split(x, y):
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
(x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test) = train_test_split(
x,
y,
test_size=0.25,
random_state=123456,
)
return x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test
Cálculo de métricas de evaluación#
[3]:
def eval_metrics(y_true, y_pred):
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error, mean_squared_error, r2_score
mse = mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred)
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_true, y_pred)
r2 = r2_score(y_true, y_pred)
return mse, mae, r2
Reporte de métricas de evaluación#
[4]:
def report(estimator, mse, mae, r2):
print(estimator, ":", sep="")
print(f" MSE: {mse}")
print(f" MAE: {mae}")
print(f" R2: {r2}")
Almacenamiento del modelo#
[5]:
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Ya no se requiere con MLflow
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# def save_best_estimator(estimator):
#
# import os
# import pickle
#
# if not os.path.exists("models"):
# os.makedirs("models")
# with open("models/estimator.pickle", "wb") as file:
# pickle.dump(estimator, file)
#
Carga del modelo#
[6]:
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Ya no se requiere con MLflow
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# def load_best_estimator():
#
# import os
# import pickle
#
# if not os.path.exists("models"):
# return None
# with open("models/estimator.pickle", "rb") as file:
# estimator = pickle.load(file)
#
# return estimator
#
Entrenamiento#
[7]:
def train_estimator(alphas, l1_ratios, n_splits=5, verbose=1):
import mlflow.sklearn
from sklearn.linear_model import ElasticNet
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
import mlflow
x, y = load_data()
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = make_train_test_split(x, y)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Búsqueda de parámetros con validación cruzada
#
estimator = GridSearchCV(
estimator=ElasticNet(
random_state=12345,
),
param_grid={
"alpha": alphas,
"l1_ratio": l1_ratios,
},
cv=n_splits,
refit=True,
verbose=0,
return_train_score=False,
)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
estimator = estimator.best_estimator_
mse, mae, r2 = eval_metrics(y_test, y_pred=estimator.predict(x_test))
if verbose > 0:
report(estimator, mse, mae, r2)
with mlflow.start_run():
params = estimator.get_params()
mlflow.log_param("alpha", params["alpha"])
mlflow.log_param("l1_ratio", params["l1_ratio"])
mlflow.log_metric("mse", mse)
mlflow.log_metric("mae", mae)
mlflow.log_metric("r2", r2)
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(estimator, "model")
[8]:
import numpy as np
train_estimator(
alphas=np.linspace(0.0001, 0.5, 10),
l1_ratios=np.linspace(0.0001, 0.5, 10),
n_splits=5,
verbose=1,
)
ElasticNet(alpha=0.0001, l1_ratio=0.16673333333333332, random_state=12345):
MSE: 0.4555342217989927
MAE: 0.5292810437627216
R2: 0.34641239384627454
MLflow ui#
Para visualizar la interfase use:
mlflow ui
Nota: En docker usar:
mlflow ui --host 0.0.0.0
con:
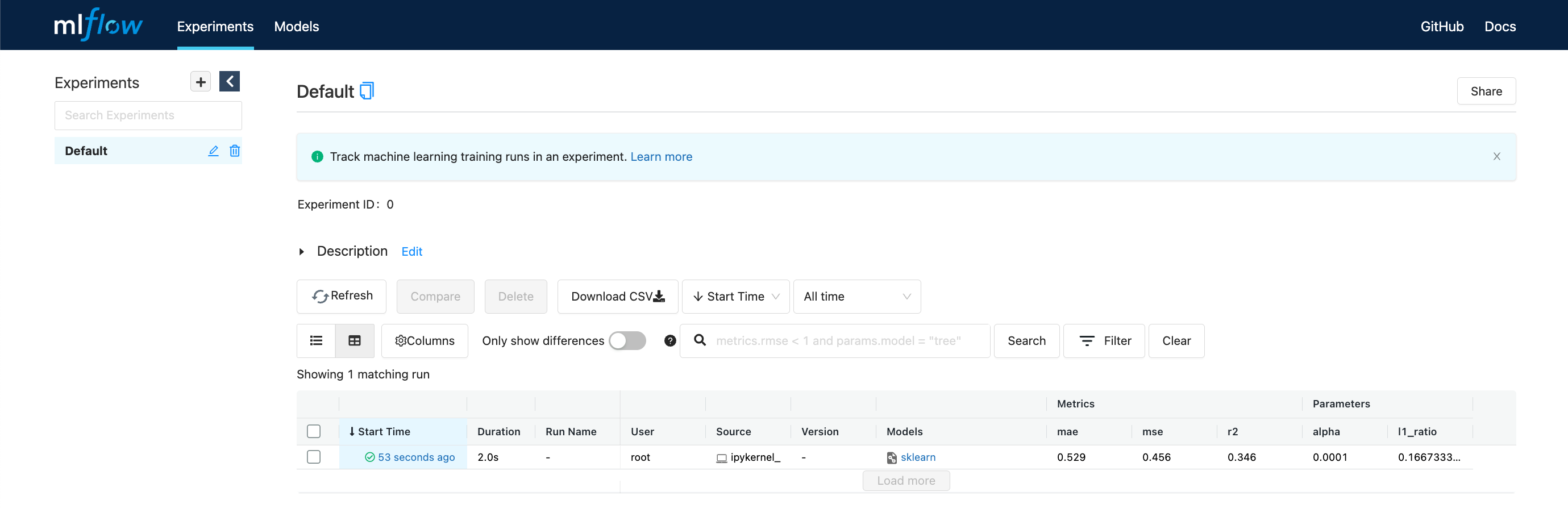
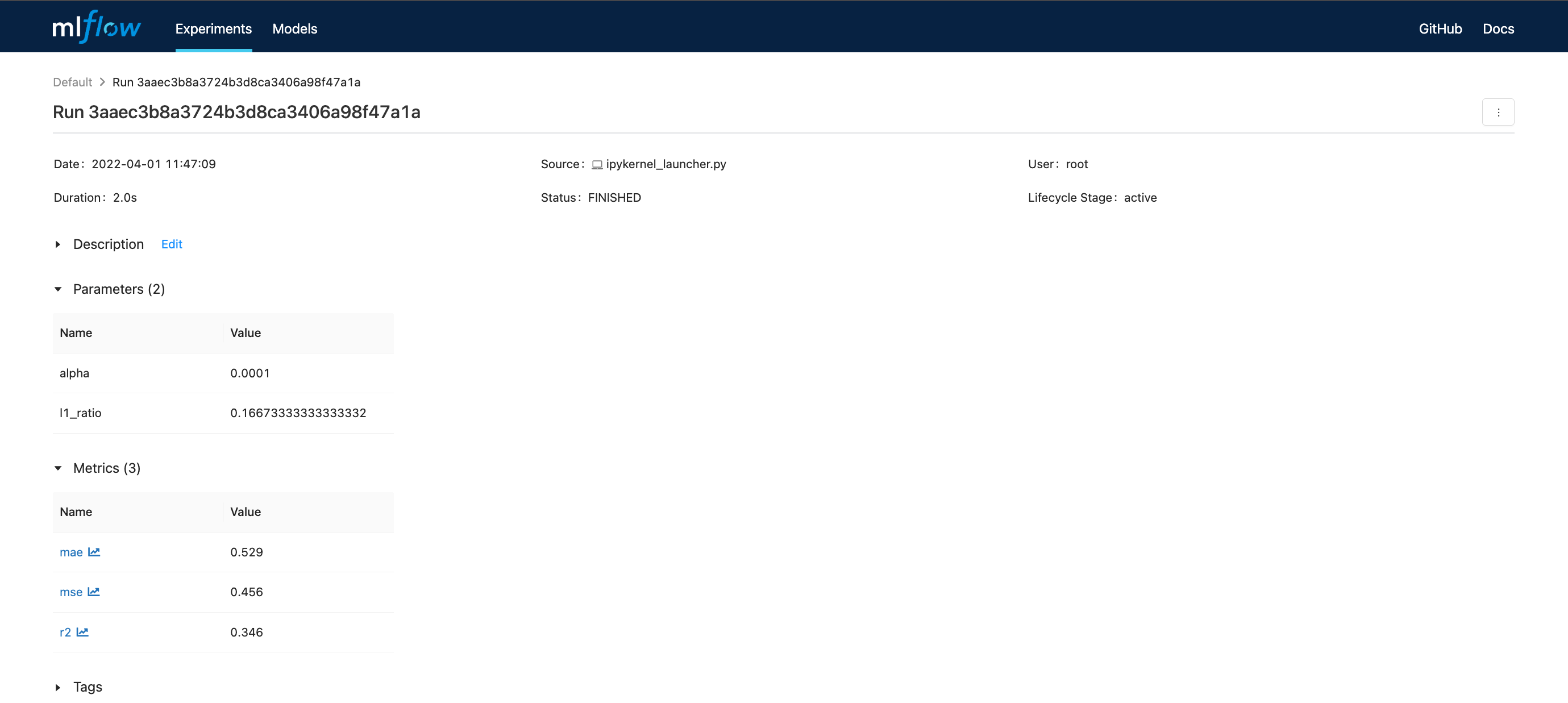
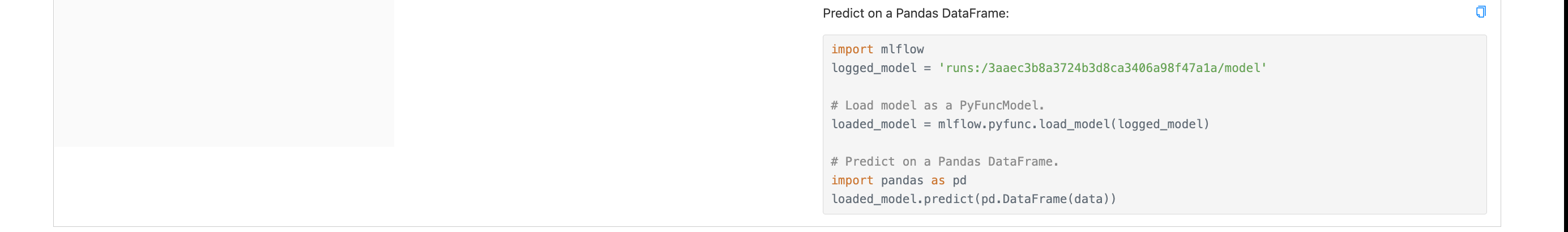
Detalles de la corrida
Chequeo#
[ ]:
def check_estimator():
import mlflow
x, y = load_data()
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = make_train_test_split(x, y)
# NOTA: este parámetro es copiado directamente de la interfase de MLflow
estimator_path = "runs:/3aaec3b8a3724b3d8ca3406a98f47a1a/model"
estimator = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model(estimator_path)
mse, mae, r2 = eval_metrics(y_test, y_pred=estimator.predict(x_test))
report(estimator, mse, mae, r2)
#
# Debe coincidir con el mejor modelo encontrado en la celdas anteriores
#
check_estimator()
[10]:
%%bash
rm -rf outputs mlruns models