Matriz de confusión#
Es una matriz que permite visualizar el desempeño de un clasificador.
La organización típica es la presentada a continuación:
| Pronóstico
| PP PN
---------|------------
P | TP FN
Real |
N | FP TN
P - Positive TP - Verdadero positivo (correcto)
N - Negative TN - Verdadero negativo (correcto)
PP - Predicted Positive FN - Falso negativo (mal clasificado)
PN - Predicted Negative FP - Falso positivo (mal clasificado)
[1]:
#
# Cálculo a partir de los valores reales y los pronósticos
#
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
y_true = [1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
y_pred = [1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
#
# | Pronostico
# | 0 1
# --------|-----------
# 0 | 10 1
# Real |
# 1 | 3 1
#
confusion_matrix(
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Ground truth (correct) target values.
y_true=y_true,
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Estimated targets as returned by a classifier.
y_pred=y_pred,
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# List of labels to index the matrix.
labels=None,
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Normalizes confusion matrix over the true (rows), predicted (columns)
# conditions or all the population.
# 'true', 'pred', 'all'
normalize=None,
)
[1]:
array([[10, 1],
[ 3, 1]])
[2]:
confusion_matrix(
y_true=y_true,
y_pred=y_pred,
labels=[1, 0],
normalize=None,
)
[2]:
array([[ 1, 3],
[ 1, 10]])
[3]:
import pandas as pd
pd.DataFrame(
confusion_matrix(
y_true=y_true,
y_pred=y_pred,
labels=[1, 0],
normalize=None,
),
columns=["PP=1", "PF=0"],
index=["P=1", "F=0"],
)
#
# | Pronóstico
# | PP PN
# ---------|------------
# P | TP FN
# Real |
# N | FP TN
#
[3]:
| PP=1 | PF=0 | |
|---|---|---|
| P=1 | 1 | 3 |
| F=0 | 1 | 10 |
[4]:
#
# Extracción de los elementos de la matriz de confusión
#
tn, fp, fn, tp = confusion_matrix(
y_true=y_true,
y_pred=y_pred,
).ravel()
display(
tn,
fp,
fn,
tp,
)
10
1
3
1
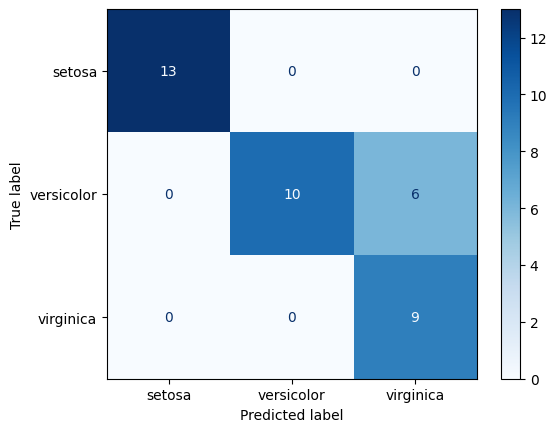
Matriz de confusión para más de dos clases#
[5]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets, svm
from sklearn.metrics import ConfusionMatrixDisplay
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
class_names = iris.target_names
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
classifier = svm.SVC(kernel="linear", C=0.01).fit(X_train, y_train)
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
disp = ConfusionMatrixDisplay.from_estimator(
classifier,
X_test,
y_test,
display_labels=class_names,
cmap=plt.cm.Blues,
normalize=None,
)
print(disp.confusion_matrix)
plt.show()
[[13 0 0]
[ 0 10 6]
[ 0 0 9]]
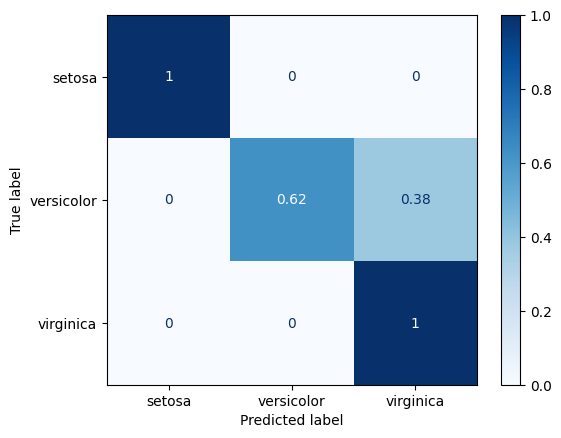
Normalización#
[6]:
#
# Normalización sobre las filas (true)
#
ConfusionMatrixDisplay.from_estimator(
classifier,
X_test,
y_test,
display_labels=class_names,
cmap=plt.cm.Blues,
normalize="true",
)
plt.show()
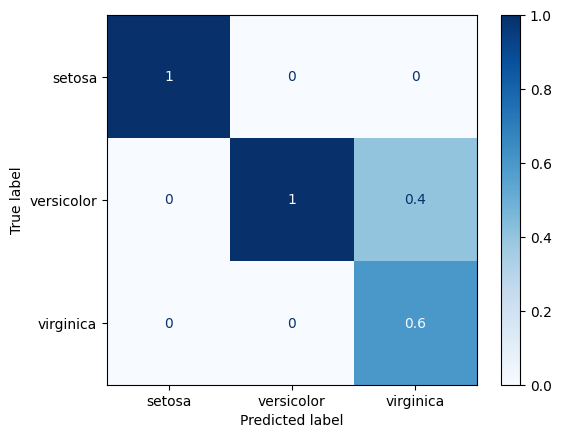
[7]:
#
# Normalización sobre las columnas (pred)
#
ConfusionMatrixDisplay.from_estimator(
classifier,
X_test,
y_test,
display_labels=class_names,
cmap=plt.cm.Blues,
normalize="pred",
)
plt.show()
[8]:
#
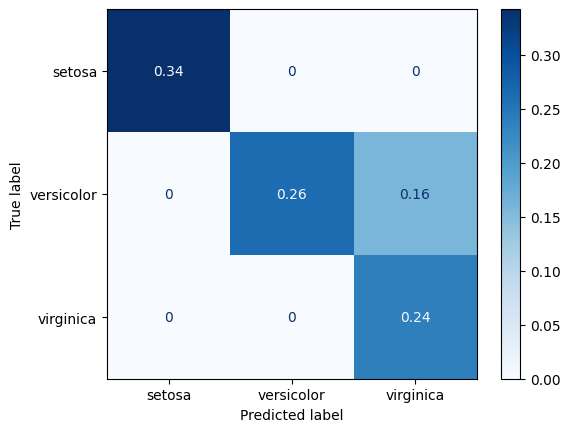
# Normalización sobre todos los datos
#
ConfusionMatrixDisplay.from_estimator(
classifier,
X_test,
y_test,
display_labels=class_names,
cmap=plt.cm.Blues,
normalize="all",
)
plt.show()