Clasificador Pasivo Agresivo#
Implementa una familia de algoritmos para grandes volumenes de datos.
Son similares al perceptrón y no requieren tasa de aprendizaje.
Incluyen un parámetro de regularización C.
Opera bajo el mismo principio del gradiente descendente estocástico.
Solo permite las funciones de pérdida Hinge y Hinge2.
hinge:L\left(y, f(x_i) \right) = \max (0, 1 - y_i f(x_i))
squared hinge:L\left(y, f(x_i) \right) = [\max (0, 1 - y_i f(x_i)]^2
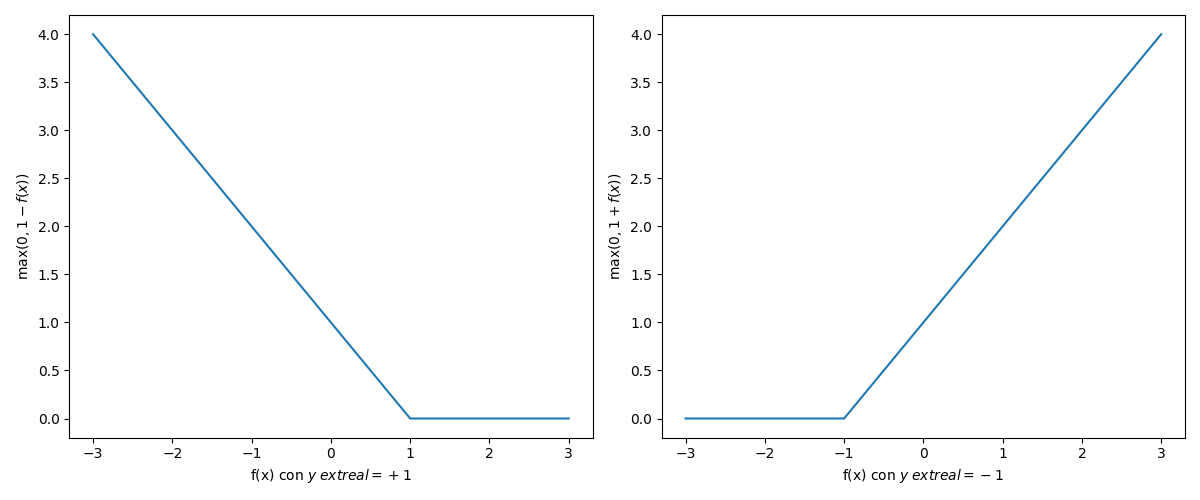
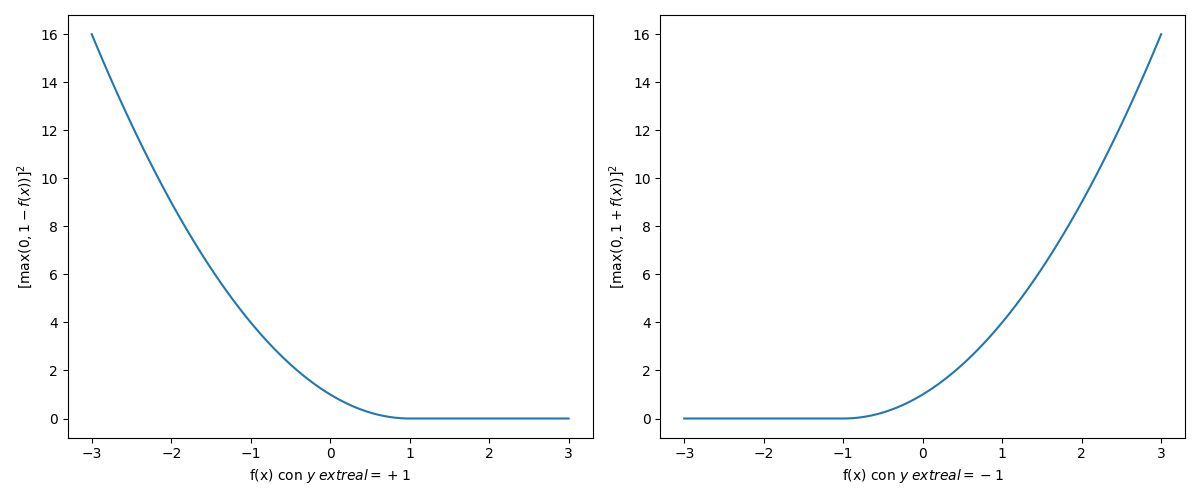
Se asume que y \in \{-1, + 1\}.
[1]:
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
X, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True)
[2]:
from sklearn.linear_model import PassiveAggressiveClassifier
passiveAggressiveClassifier = PassiveAggressiveClassifier(
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Maximum step size (regularization).
C=1.0,
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Whether the intercept should be estimated or not. If False, the data is
# assumed to be already centered.
fit_intercept=True,
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The maximum number of passes over the training data (aka epochs).
max_iter=1000,
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Tolerance for stopping criteria.
tol=0.0001,
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Whether to use early stopping to terminate training when validation.
# score is not improving. If set to True, it will automatically set aside a
# stratified fraction of training data as validation and terminate training
# when validation score is not improving by at least tol for n_iter_no_change
# consecutive epochs.
early_stopping=False,
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The proportion of training data to set aside as validation set for early
# stopping. Must be between 0 and 1. Only used if early_stopping is True.
validation_fraction=0.1,
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Number of iterations with no improvement to wait before early stopping.
n_iter_no_change=5,
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Whether or not the training data should be shuffled after each epoch.
shuffle=True,
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The loss function to be used hinge: equivalent to PA-I in the reference
# paper. squared_hinge: equivalent to PA-II in the reference paper.
loss="hinge",
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Used to shuffle the training data, when shuffle is set to True.
random_state=None,
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# When set to True, reuse the solution of the previous call to fit as
# initialization, otherwise, just erase the previous solution.
warm_start=False,
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Preset for the class_weight fit parameter. Weights associated with
# classes. If not given, all classes are supposed to have weight one.
#
# The “balanced” mode uses the values of y to automatically adjust weights
# inversely proportional to class frequencies in the input data as
# n_samples / (n_classes * np.bincount(y)).
class_weight=None,
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# When set to True, computes the averaged SGD weights and stores the result
# in the coef_ attribute. If set to an int greater than 1, averaging will
# begin once the total number of samples seen reaches average. So
# average=10 will begin averaging after seeing 10 samples.
average=False,
)
passiveAggressiveClassifier.fit(X, y)
passiveAggressiveClassifier.predict(X)
[2]:
array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,
1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0,
1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1,
0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1])
[3]:
passiveAggressiveClassifier.intercept_
[3]:
array([0.00068508])
[4]:
passiveAggressiveClassifier.coef_
[4]:
array([[ 4.63457700e-03, 7.04383499e-03, 2.62210835e-02,
1.13297897e-02, 4.50206338e-05, -3.88603635e-05,
-1.05415563e-04, -4.58620495e-05, 8.91650814e-05,
3.83417044e-05, 8.60646190e-05, 6.08083072e-04,
3.10388565e-04, -4.82872538e-03, 4.65852986e-06,
-8.43339916e-06, -9.72937666e-06, -1.95109607e-06,
1.01797580e-05, 9.52358712e-07, 4.83237856e-03,
7.54592480e-03, 2.54822744e-02, -1.37611604e-02,
5.50130520e-05, -1.96603439e-04, -2.90404168e-04,
-7.80318861e-05, 9.82485882e-05, 2.74353123e-05]])
[5]:
passiveAggressiveClassifier.score(X, y)
[5]:
0.8541300527240774
[5]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def hinge():
fx = np.linspace(-3, 3, 100)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(fx, np.where(1-fx>0,1-fx, 0))
plt.xlabel("f(x) con $y_\text{real}=+1$")
plt.ylabel("$\max (0, 1 - f(x))$")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(fx, np.where(1+fx>0,1+fx, 0))
plt.xlabel("f(x) con $y_\text{real}=-1$")
plt.ylabel("$\max (0, 1 + f(x))$")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("assets/hinge.png")
plt.close()
# hinge()
[6]:
def hinge2():
fx = np.linspace(-3, 3, 100)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(fx, np.where(1-fx>0,np.power(1-fx, 2), 0))
plt.xlabel("f(x) con $y_\text{real}=+1$")
plt.ylabel("$[\max (0, 1 - f(x))]^2$")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(fx, np.where(1+fx>0,np.power(1+fx, 2), 0))
plt.xlabel("f(x) con $y_\text{real}=-1$")
plt.ylabel("$[\max (0, 1 + f(x))]^2$")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("assets/hinge2.png")
plt.close()
hinge2()