La función make_blobs — 7:11 min#
7:11 min | Ultima modificación: Septiembre 27, 2021 | YouTube
La función make_blobs de scikit-learn se usa para generar clusters de datos n-dimensionales, los cuales son usados para probar algoritmos de clustering y clasificación. En esta lección se describe el uso de esta función.
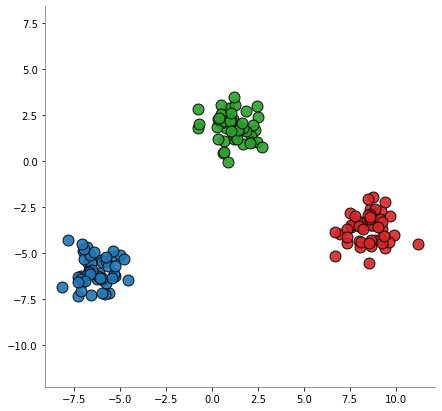
[1]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
X, y = make_blobs(
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# If int, it is the total number of points equally divided among clusters.
# If array-like, each element of the sequence indicates the number of
# samples per cluster
n_samples=150,
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The number of features for each sample.
n_features=2,
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The number of centers to generate, or the fixed center locations.
centers=3,
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The standard deviation of the clusters.
cluster_std=0.8,
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The bounding box for each cluster center when centers are generated at
# random.
center_box=(-10, 10),
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Shuffle the samples.
shuffle=False,
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Determines random number generation for dataset creation.
random_state=12345,
)
plt.figure(figsize=(7, 7))
plt.scatter(
X[:50, 0],
X[:50, 1],
color="tab:red",
edgecolors="k",
s=120,
alpha=0.9,
)
plt.scatter(
X[50:100, 0],
X[50:100, 1],
color="tab:blue",
edgecolors="k",
s=120,
alpha=0.9,
)
plt.scatter(
X[100:, 0],
X[100:, 1],
color="tab:green",
edgecolors="k",
s=120,
alpha=0.9,
)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_color("gray")
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_color("gray")
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_visible(False)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_visible(False)
plt.axis("equal")
plt.show()
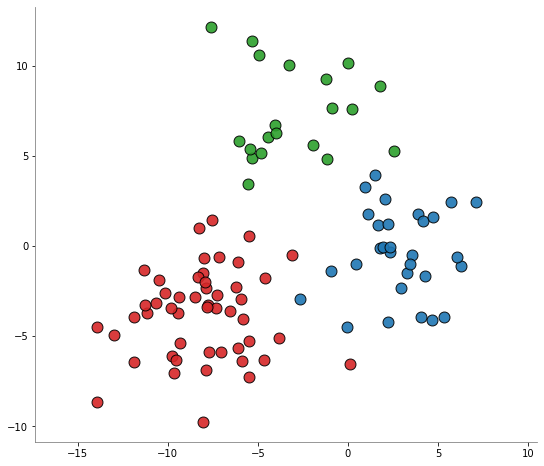
[5]:
X, y = make_blobs(
n_samples=[50, 30, 20],
n_features=2,
centers=[
[-8, -4],
[3, 0],
[-3, 7],
],
cluster_std=2.5,
center_box=(-10, 10),
shuffle=False,
random_state=12345,
)
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 8))
plt.scatter(
X[:50, 0],
X[:50, 1],
color="tab:red",
edgecolors="k",
s=120,
alpha=0.9,
)
plt.scatter(
X[50:80, 0],
X[50:80, 1],
color="tab:blue",
edgecolors="k",
s=120,
alpha=0.9,
)
plt.scatter(
X[80:, 0],
X[80:, 1],
color="tab:green",
edgecolors="k",
s=120,
alpha=0.9,
)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_color("gray")
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_color("gray")
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_visible(False)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_visible(False)
plt.axis("equal")
plt.show()